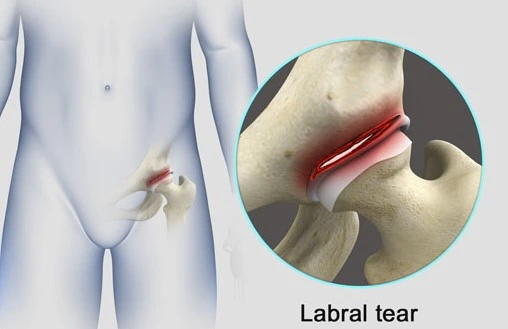
Hip labral defects refer to tears or damage in the labrum, a ring of cartilage that surrounds the hip joint. The labrum plays a crucial role in stabilizing the joint and cushioning the bones. Labral tears can occur due to traumatic injuries, repetitive motions, or degenerative changes, leading to pain, instability, and decreased range of motion in the hip.
This condition is often diagnosed in athletes or individuals engaged in activities that involve high-impact movements or twisting motions. Symptoms may include hip pain, a clicking or locking sensation, stiffness, and difficulty bearing weight. Non-surgical treatments like physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and activity modification may provide relief, but surgery is often necessary for significant tears.
Surgical intervention for hip labral defects aims to repair or reconstruct the damaged labrum to restore joint stability and alleviate pain. The procedure typically involves the following steps:
Treating hip labral defects is essential for individuals experiencing significant hip pain and dysfunction, providing a pathway to improved joint health and a return to normal activities.
