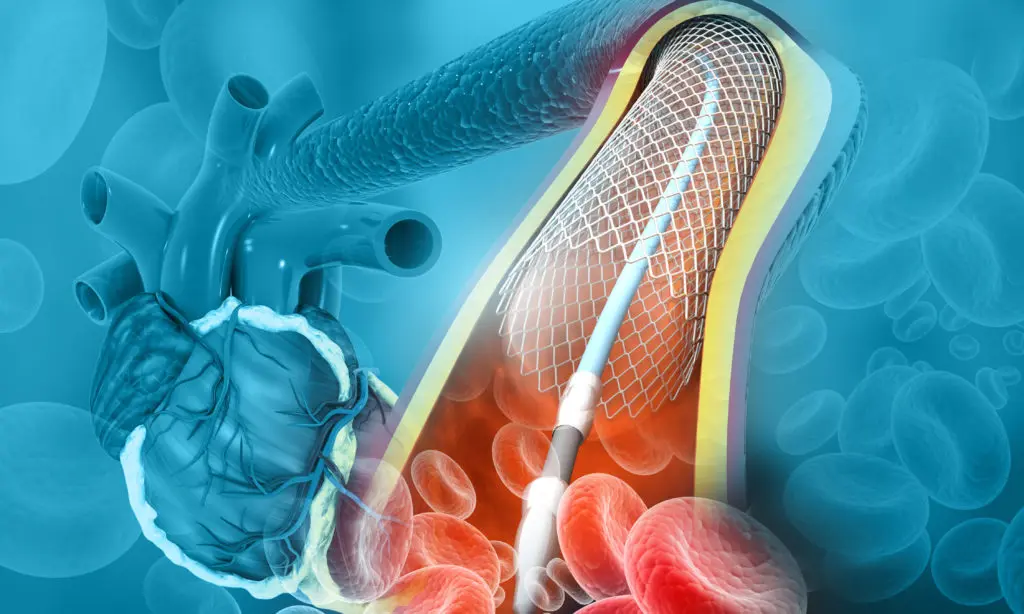
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to open blocked or narrowed arteries, typically to restore blood flow to the heart muscle or other parts of the body. It is often performed in cases of coronary artery disease, where plaque buildup restricts blood flow and increases the risk of heart attack. Angioplasty helps to relieve chest pain (angina) and reduce heart-related risks.
This procedure is commonly recommended for patients with significant arterial blockages that cause symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath. It can also be performed as an emergency treatment during a heart attack to quickly restore blood flow and limit heart damage.
During angioplasty, a small balloon is inserted into the blocked artery through a catheter and then inflated to widen the artery. A stent (a small mesh tube) may be placed to keep the artery open. The steps involved in angioplasty typically include:
Angioplasty is a proven, effective procedure for treating blocked arteries, offering patients significant relief from symptoms and reducing the risks of serious heart events.
